Intubation Skill Guide
Posted on: November 24, 2024, by : Haroon Shaukat MD| Appropriate Steps to Complete |
| Takes or verbalizes body substance isolation precautions |
| Directs assistant to pre-oxygenate patient |
| Identifies/selects proper equipment for intubation |
| Checks laryngoscope to assure operational with bulb tight |
| Places patient in neutral or sniffing position |
| Opens the airway manually |
| Inserts blade while displacing tongue |
| Elevates mandible with laryngoscope |
| Introduces ET tube and advances to proper depth |
| Directs ventilation of patient |
| Confirms proper placement by auscultation bilaterally over each lung and over epigastrium |
| Secures ET tube [may be verbalized] |
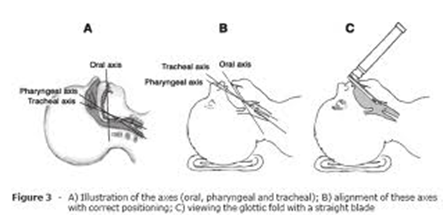
A. Types of Laryngoscope Blades
1. Straight Blades (Miller) – Preferred in Pediatrics
✅ Better control of the large, floppy epiglottis in infants and young children
✅ Useful in neonates and small infants
2. Curved Blades (Macintosh)
✅ Used more in older children and adults
✅ Sits in the vallecula to lift the epiglottis indirectly
Blade Size Guide:
| Age/Size | Blade Type | Size |
| Preterm (<1.5 kg) | Miller | 00 |
| Full-term infant | Miller | 0 |
| 1 year | Miller | 1 |
| 2–5 years | Miller | 1–2 |
| >5 years | Miller or Mac | 2–3 |

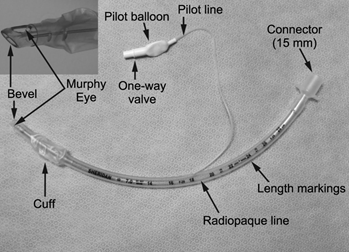
B. Types of Endotracheal Tubes (ETT)
✅ Cuffed Tubes (Common in modern practice)
- Allow better control of ventilation and reduce air leaks
- Always confirm cuff pressure <20-25 cm H₂O
✅ Uncuffed Tubes
- Previously preferred in infants <1 year (but not required with modern cuffs)
ETT Size (Uncuffed):
- Formula: (Age in years / 4) + 4
ETT Size (Cuffed):
- Formula: (Age in years / 4) + 3.5
Depth of Insertion (cm)
- Formula: (Age in years / 2) + 12
- Alternatively: ETT size × 3 (for children >1 year)
Example: 4-year-old → (4/2) + 12 = 14 cm
C. Medications for Pediatric Intubation (RSI Approach)
Pre-treatment (as needed)
- Atropine: 0.02 mg/kg IV (min 0.1 mg, max 0.5 mg) to prevent bradycardia
- Lidocaine: Rarely used; controversial in increased ICP
Sedation/Induction Agents
- Ketamine: 1-2 mg/kg IV (good for asthma, shock)
- Etomidate: 0.3 mg/kg IV (neutral on BP but caution in sepsis)
- Propofol: 1-2 mg/kg IV (hypotension risk)
Paralytics
- Succinylcholine: 1-2 mg/kg IV (contraindicated in neuromuscular disease, burns >24h old, hyperkalemia)
- Rocuronium: 1-1.2 mg/kg IV (longer duration, safer profile)
D. SOAP-ME: Pediatric Airway Preparation Mnemonic
✅ S – Suction (working, appropriately sized catheters/yankauer)
✅ O – Oxygen (pre-oxygenate, NRB or BVM with reservoir)
✅ A – Airway equipment (check blade, tube size, stylet, BVM, back-up devices like supraglottic airways)
✅ P – Pharmacy/Pharmacology (RSI meds drawn and labeled)
✅ M – Monitors (Pulse ox, cardiac monitor, BP cuff)
✅ E – End-tidal CO₂ / Esophageal Detector Device (for tube confirmation)
✅ Confirming Tube Placement
- Direct visualization of cords during intubation
- Bilateral breath sounds
- Absence of gastric sounds
- Continuous waveform capnography (gold standard)
- Chest X-ray if needed: Tube tip 2 cm above the carina
(Ideally, double black line on uncuffed ETT should be at vocal cords or cuff should be past vocal cords.)
E. Sources to Visualize